Anionic Polymerization Of Vinyl Chloride
Arihiro kanazawa shokyoku kanaoka and sadahito aoshima.
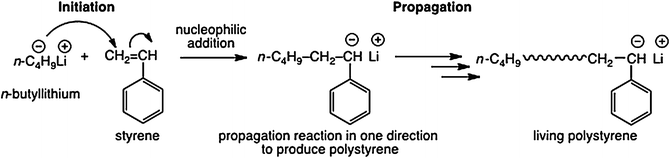
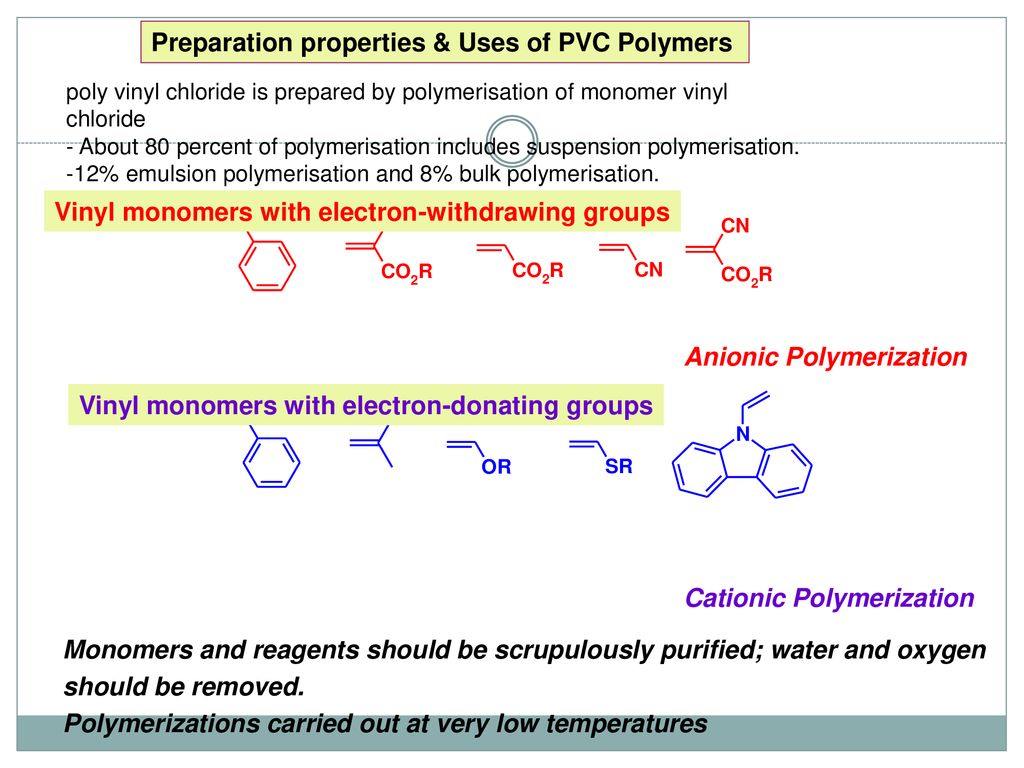
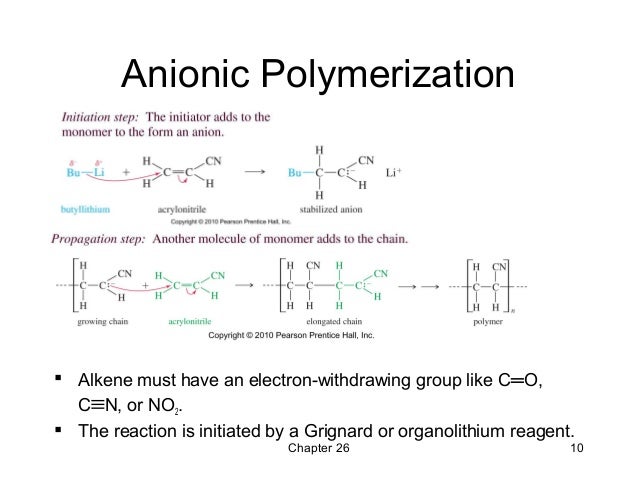
Anionic polymerization of vinyl chloride. Free radical polymerization frp is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free radical building blocks. The type of reaction has many manifestations but traditionally vinyl monomers are used. Sklizkova institute of macromolecula compounds u s s r. Polymerization of vinyl chloride with butyllithium and its complexes v.
Copolymerization initiated by n butyllithium. Often anionic polymerization involves living polymerizations which allows control of structure and composition. That is small molecules containing carbon carbon double bonds. Relationship between polymerization behavior and the nature of lewis acids.
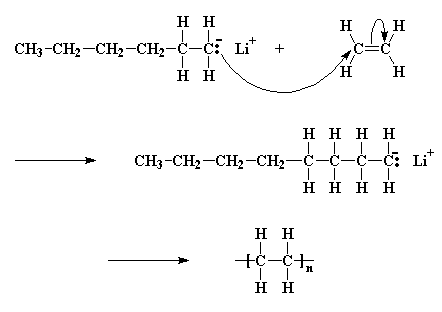
Free radicals can be formed by a number of different mechanisms usually involving separate initiator molecules. Anionic polymerization of vinyl chloride has been studied. Anionic polymerization of vinylidene chloride. The mechanism of radical polymerization is illustrated below for the polymerization of chloroethene vinyl chloride.
Of the organometallic compounds tested as initiators only butyllithium was found to initiate polymerization. They make up largest family of polymers. Academy of sciences received 10 january 1967 in the anionic polymerization of vinyl chloride vc especially with lithium alkyls ill the termination step is a major factor and this leads to rapid slowing dowel of the. Macromolecules 2010 43 6 2739 2747.
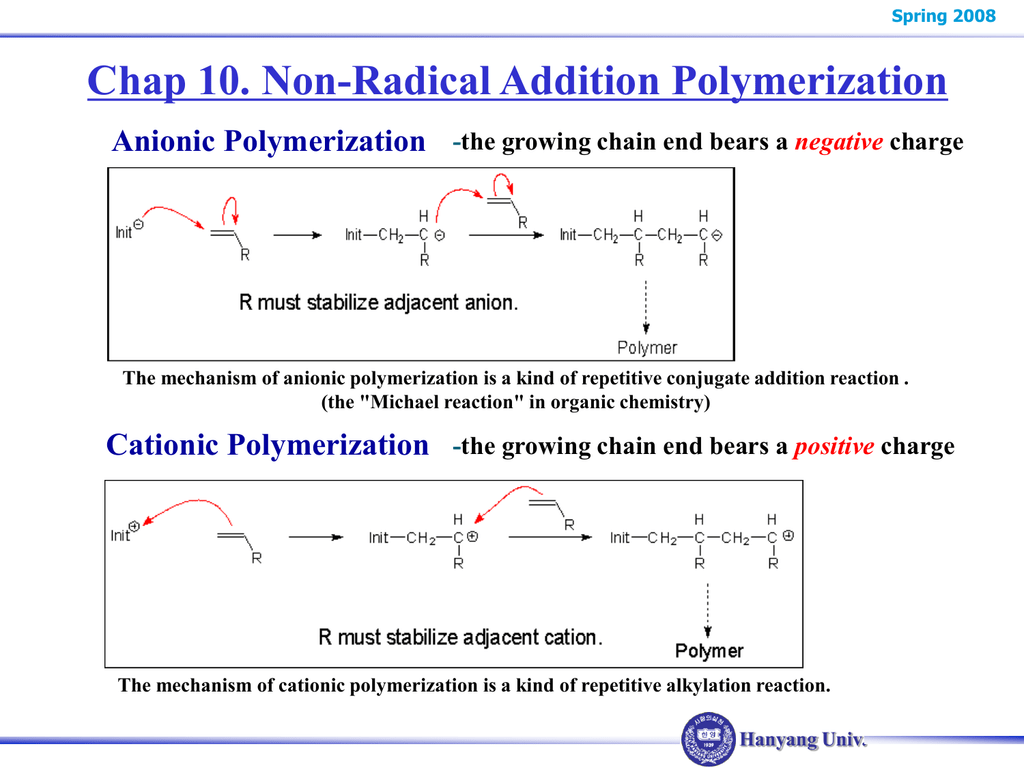
Anionic addition polymerization is a form of chain growth polymerization or addition polymerization that involves the polymerization of monomers initiated with anions. Polymerization in bulk at 0 c. B data of talamini et a1 21y22 radical 50 cb radical 0. Bulletin of the chemical society of japan 1962 35 3 395 399.
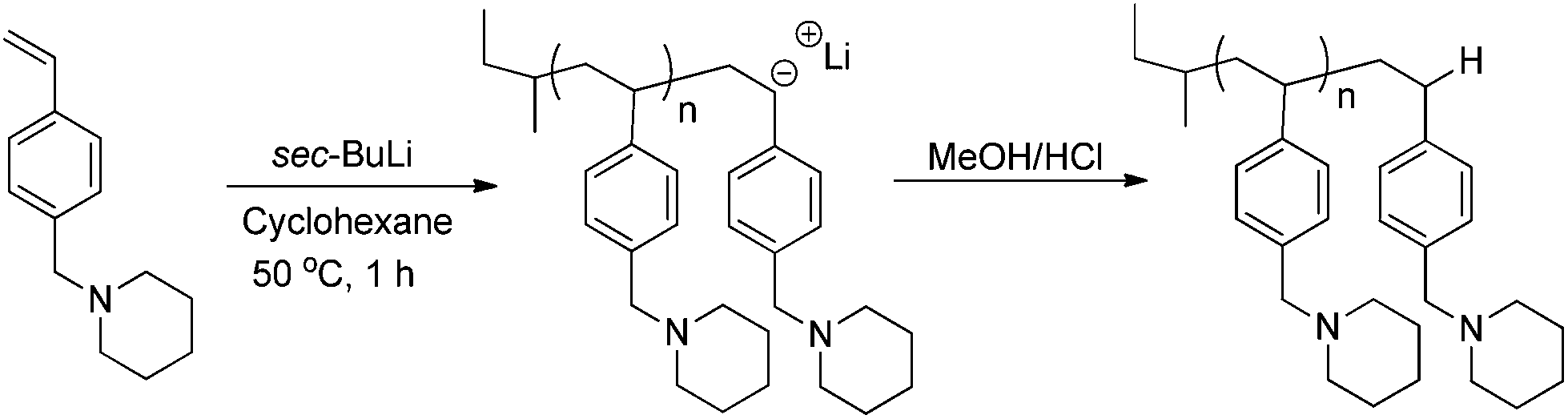
Anionic polymerization of vinyl chloride table iv chain branching in pvc prepared by anionic and radical polymerization sample mn chj1000 c atoms 2a 3a 4a a chain branching of these samples determined by dr. Thus in this chapter general aspects of cationic polymerization are discussed followed by a brief overview of early development of living cationic polymerization. Cationic polymerization of polar monomers such as vinyl ethers and styrene derivatives played a critical role in accomplishing ideal living cationic polymerization of vinyl type monomers. Q as is typical for initiating radical reactions an initiator usually a peroxide is employed.
Q the repeat structure of the final polymer is written as. Anionic polymerization of vinylidene chloride. Following its generation the initiating free radical adds nonradical monomer units thereby growing the polymer chain.