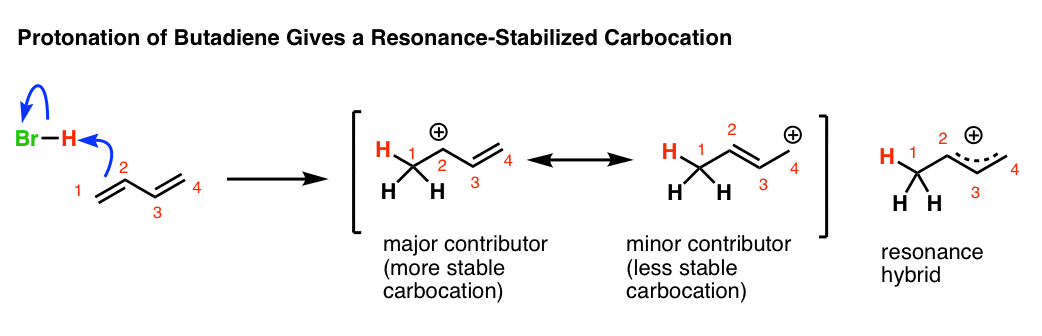
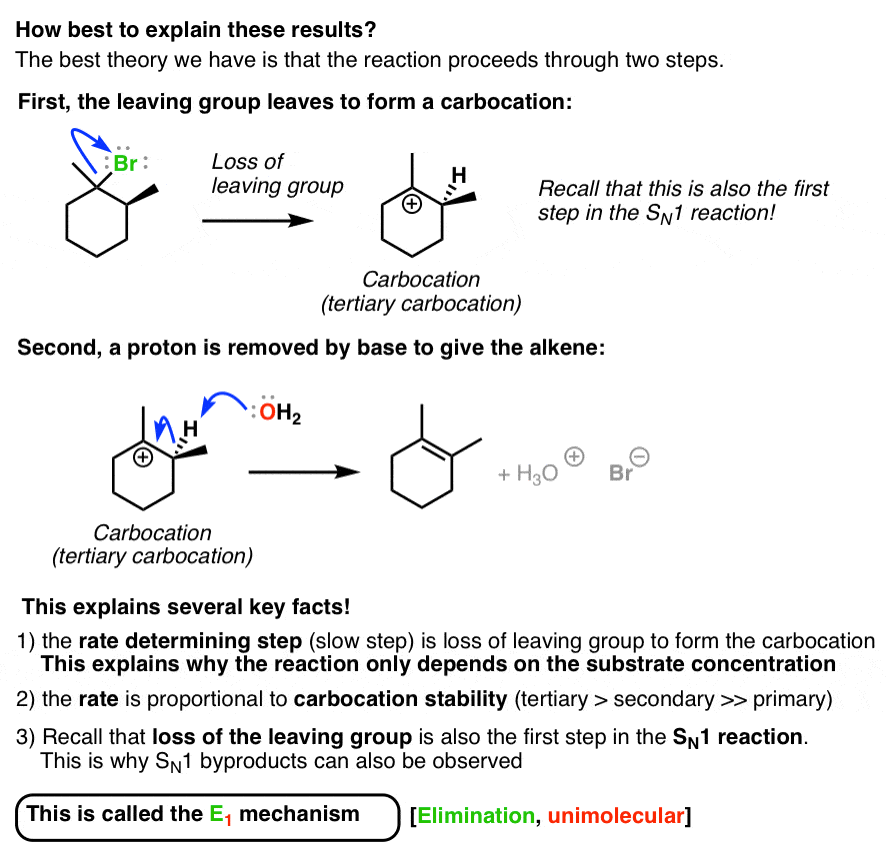
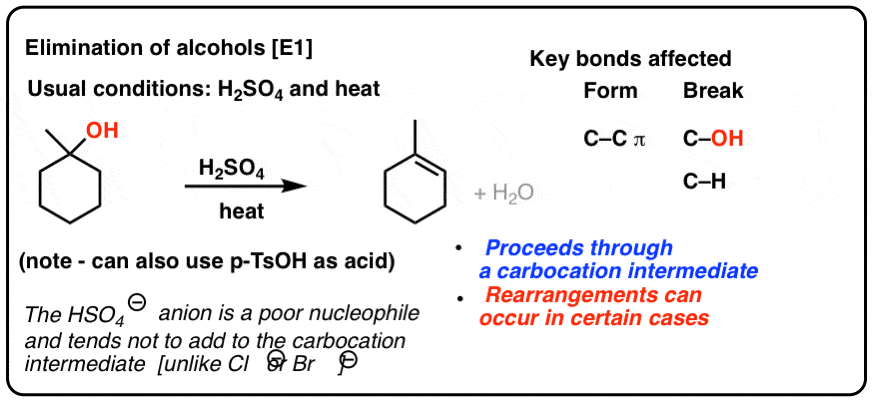
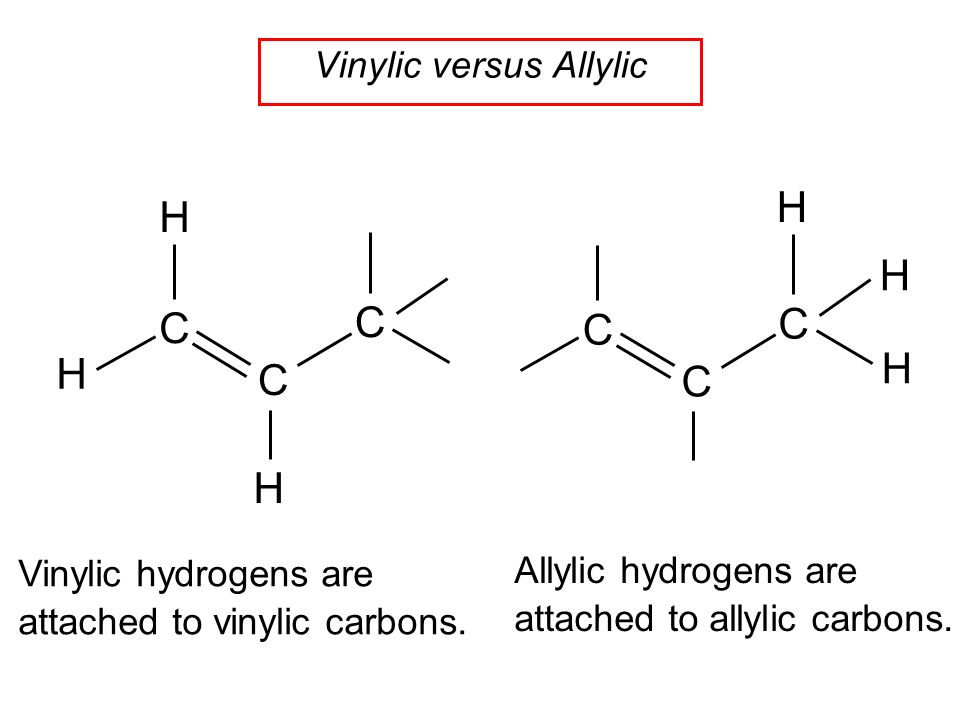
Allylic Vs Vinylic Carbocation

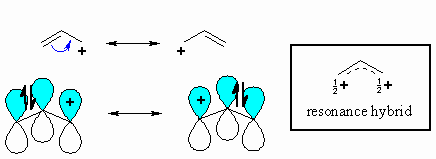
An allylic carbocation in which an allylic carbon bears the positive charge.
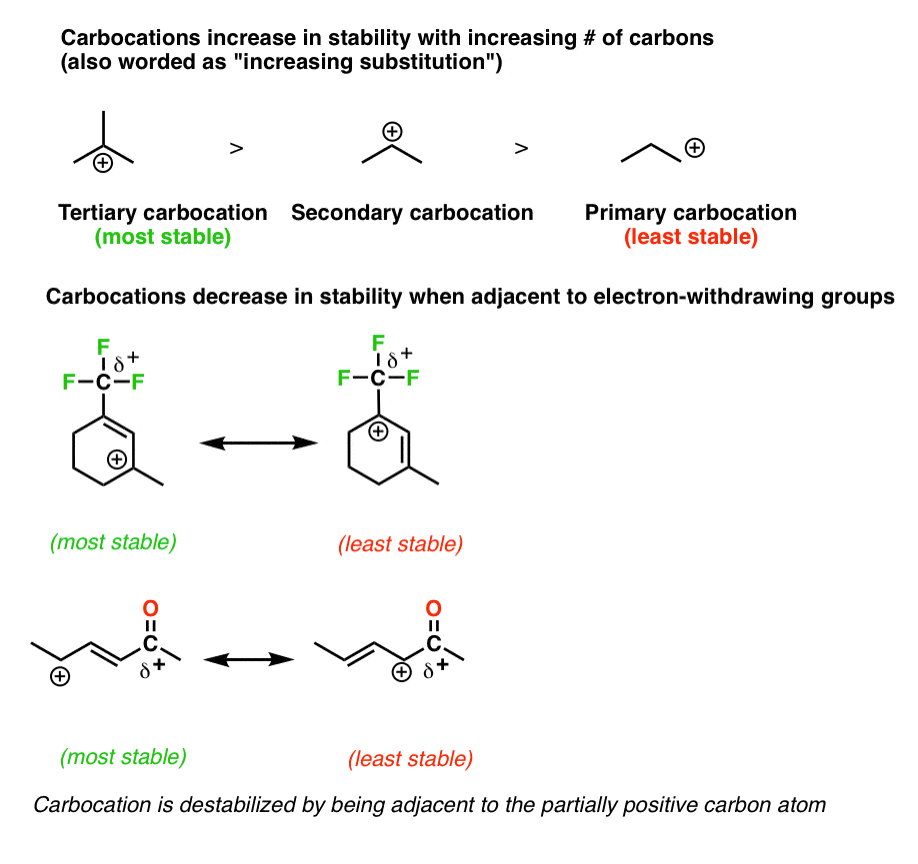
Allylic vs vinylic carbocation. What is vinylic carbon. An allylic system has a minimum of 3 carbons. In the tertiary carbocation shown above the three alkyl groups help to stabilize the positive charge. The allylic carbon and the nearby double bond.
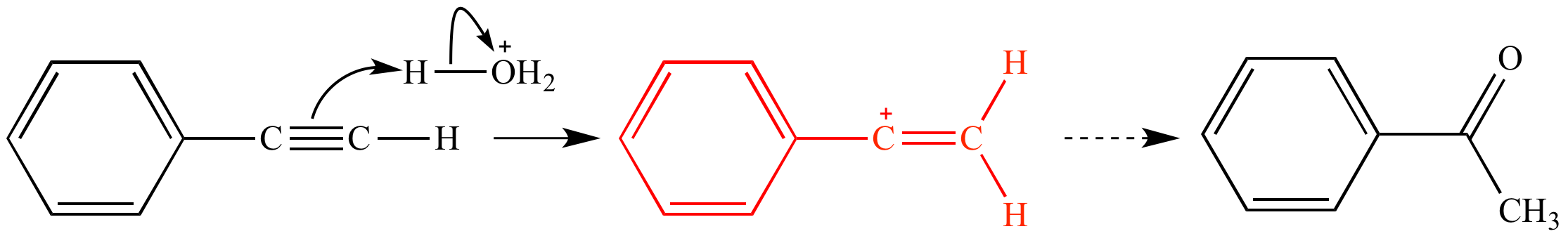
The overall charge on the carbocation remains unchanged but some of the charge is now carried by the alkyl groups attached to the central carbon atom. An allylic carbon is one that is directly attached to a pi bond. A vinyl carbocation has a positive charge on the same carbon as the double bond. As expected from its sp hybridization the vinyl cation prefers a linear geometry.
Due to the stability of the carbocation allyl compounds radially form intermediates during the reaction. Compounds related to the vinyl cation include allylic carbocations and benzylic carbocations as well as aryl carbocations. That is the charge has been dispersed. It is sp 2 hybridized.
Allyl form a stable carbocation because of the electron delocalization. Vinylic carbon is a carbon that is involved in a double bond with another carbon. An allylic carbocation is a resonance stabilized carbocation in each of the two resonance forms of which the formal charge of 1 is on an allylic carbon. For example s n 1 reaction.
The double bonded carbon atoms can be classified as vinylic and allylic carbon atoms. N1 reactions of allylic halides allylic halides and sulfonates are more reactive toward than simple alkyl halides toward nucleophilic substitution by the s n1 mechanism cc hc h h ch 3 ch 3 cc hc h h cl ch 3 ch 3 h h cc hc h h oh ch 3 ch 3 cc cch 3 ch 3 h oh h h cc cch 3 ch 3 h cl h h resonance stabilized carbocation intermediate over 100x. Do not confuse an allylic group with a vinyl group. Vinylic carbon makes a double bond with another carbon which is also sp 2 hybridized.
Vinylic carbocations are unstable as they lack p character.