Allylic And Vinylic Position
The allylic carbon atom is more reactive than normal.
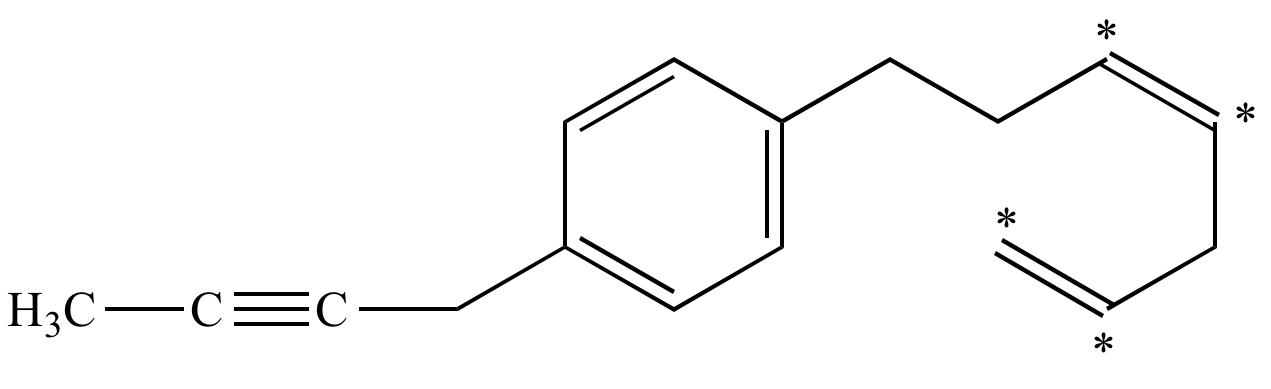
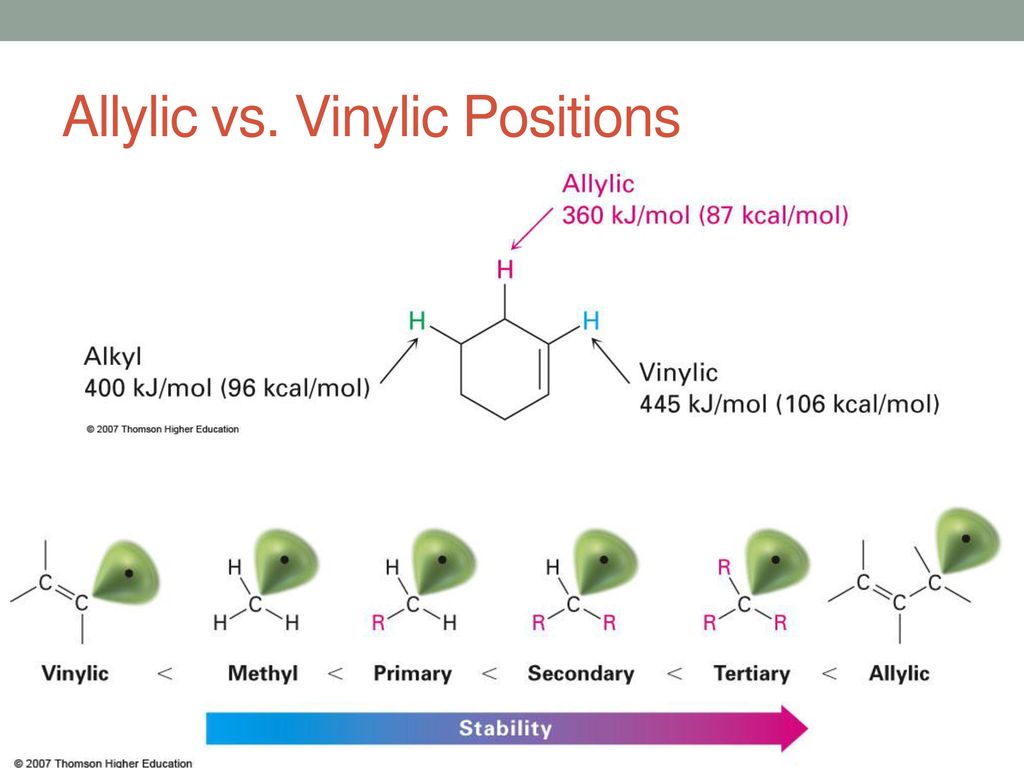
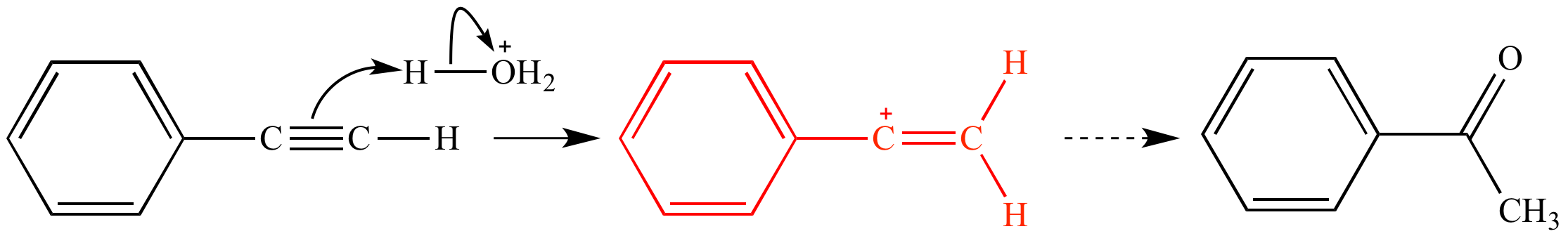
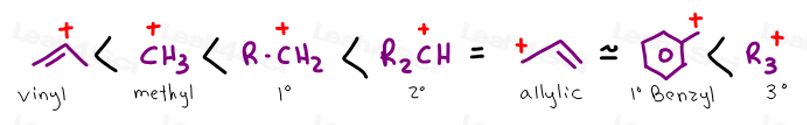
Allylic and vinylic position. As the table below shows the dissociation energy for the allylic c h bond is lower than the dissociation energies for the c h bonds at the vinylic and alkylic positions. The positions adjacent to alkene c c often show enhanced reactivity compared to simple alkanes due to the proximity of the adjacent π system. This molecule has four vinyl ic positions each marked with. This is because the radical formed when the allylic hydrogen is removed is resonance stabilized.
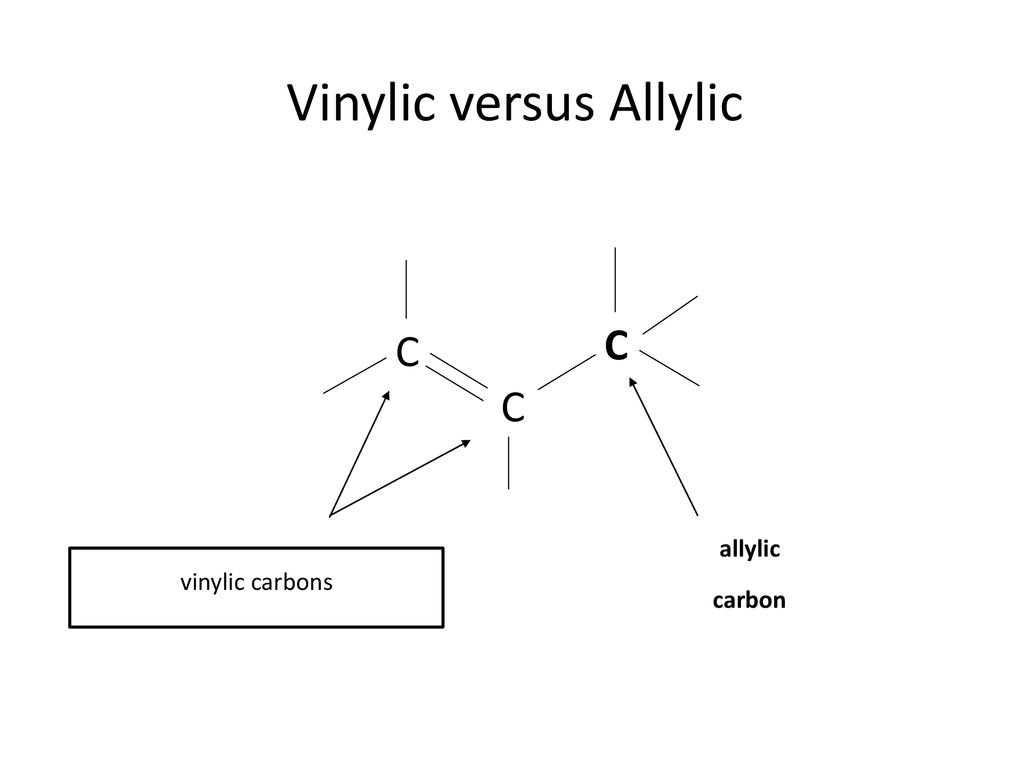
Allyl have two sp 2 hybridized carbon atoms and one sp 3 hybridized carbon atom. In a molecule the position next to an alkene. The allylic position is the one on carbon next to double bond. Hence given that the halogen.
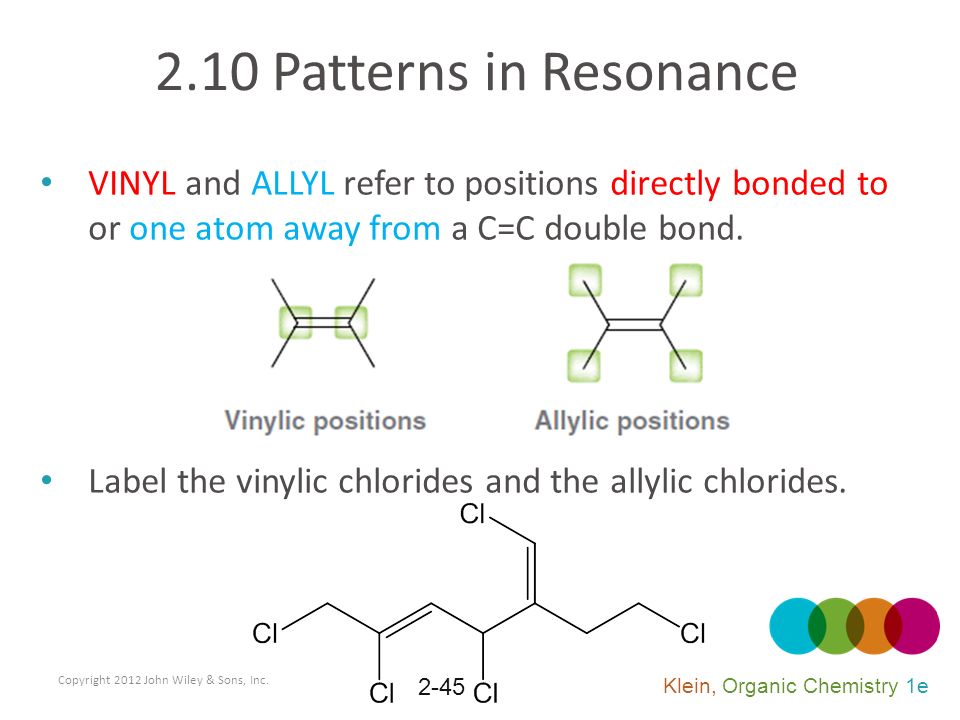
The allylic positions are labeled with asterisks. A better question would be what s an allylic position because allylic proton is nothing more than proton hydrogen in allylic position. Why substitution of allylic hydrogens. The allylic position is also like a vinylic position.
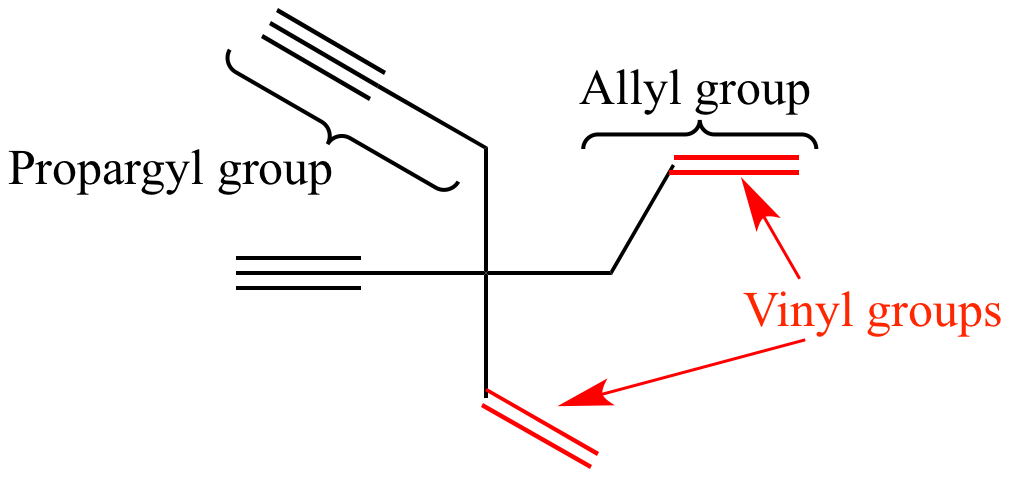
Allyl group benzylic position propargylic position vinylic position alkene. The general formula for allyl is r ch 2 ch ch 2 in which the asterisk carbon atom is an allylic carbon atom. Allyl indicates a functional group with structural formula h 2 c ch ch 2 r where r is the rest of the molecule it consists of methylene bridge ch 2 in between the vinyl group ch ch 2 and the rest of the molecule therefore allyl group contains sp 2 hybridized vinyl carbon atoms and sp 3 hybridized allyl carbon atom. The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon.
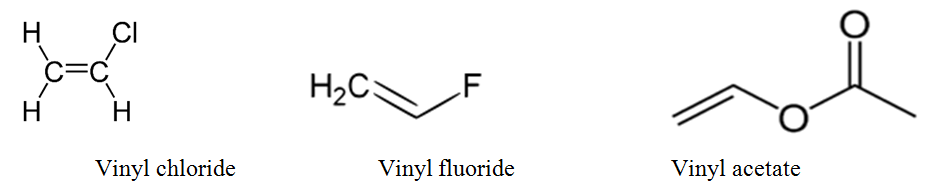
Lewis structure of vinyl chloride a vinyl ic halide. It would be kept mentioned that allyl is the latin word that is used for the garlic allium sativum. Such positions are referred as allylic in contrast recall that the term vinylic is used to described the atoms directly associated with the c c unit. Allyl is a name for this radical.
Return to glossary index. On or bonded to the carbon of an alkene.