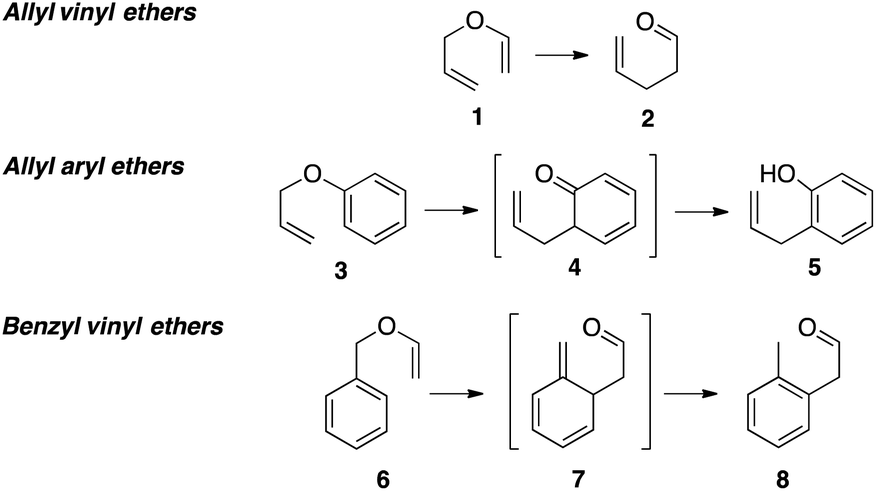
Allyl And Vinyl Position
Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule.
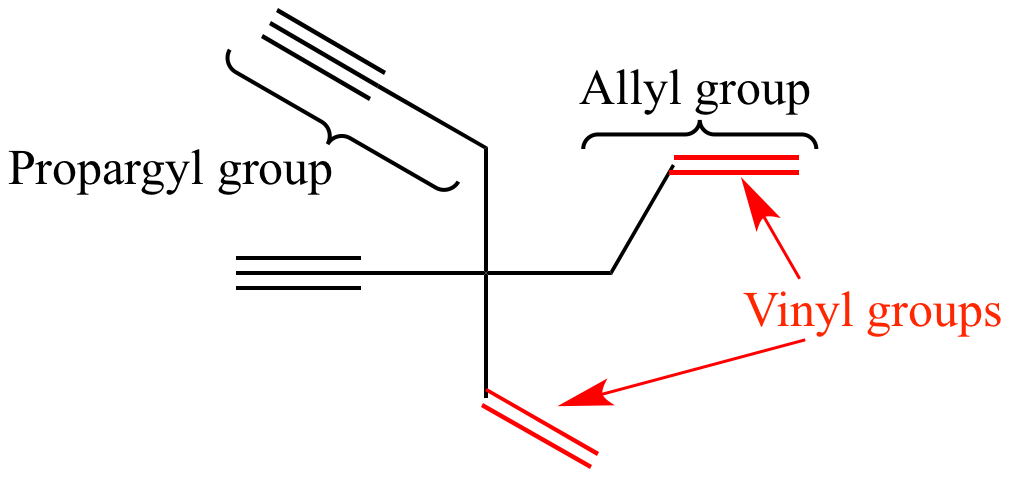
Allyl and vinyl position. The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon. Allyl group holds three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms which gets attached to any other group of atoms through ch 2 group. An allyl derivative was first found within the garlic oil by theodor wertheim in 1844 he named it schwefelallyl. It consists of a methylene bridge ch 2 attached to a vinyl group ch ch 2.
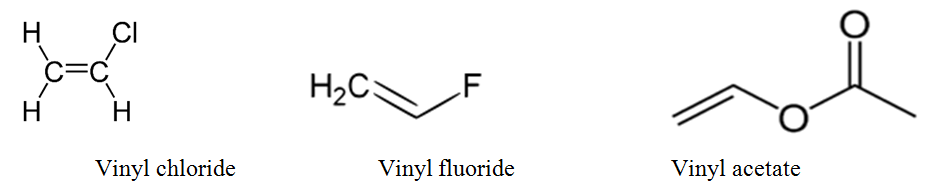
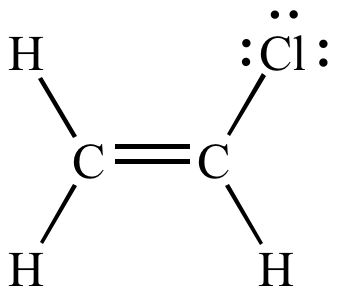
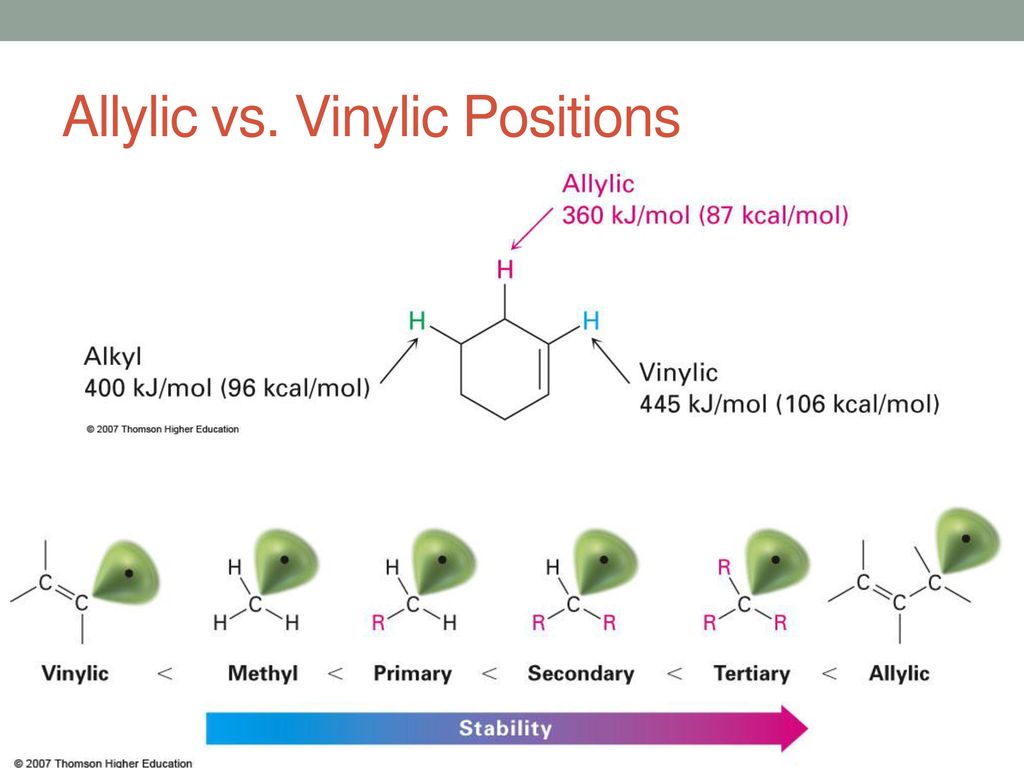
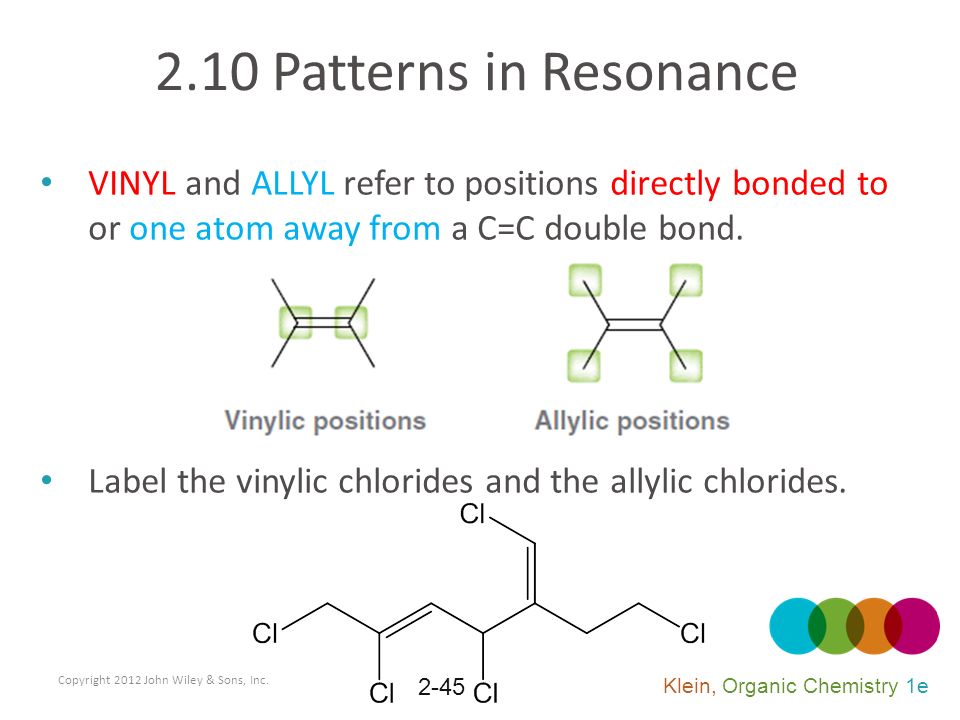
Lewis structure of vinyl chloride a vinyl ic halide. Allylic position is the same as allylic carbon similarly for vinylic and benzylic so the stability of carbocations goes as. Both groups own a double bond between two carbon atoms where all the other atoms are bonded through single bonds. This molecule has four vinylic positions each marked with.
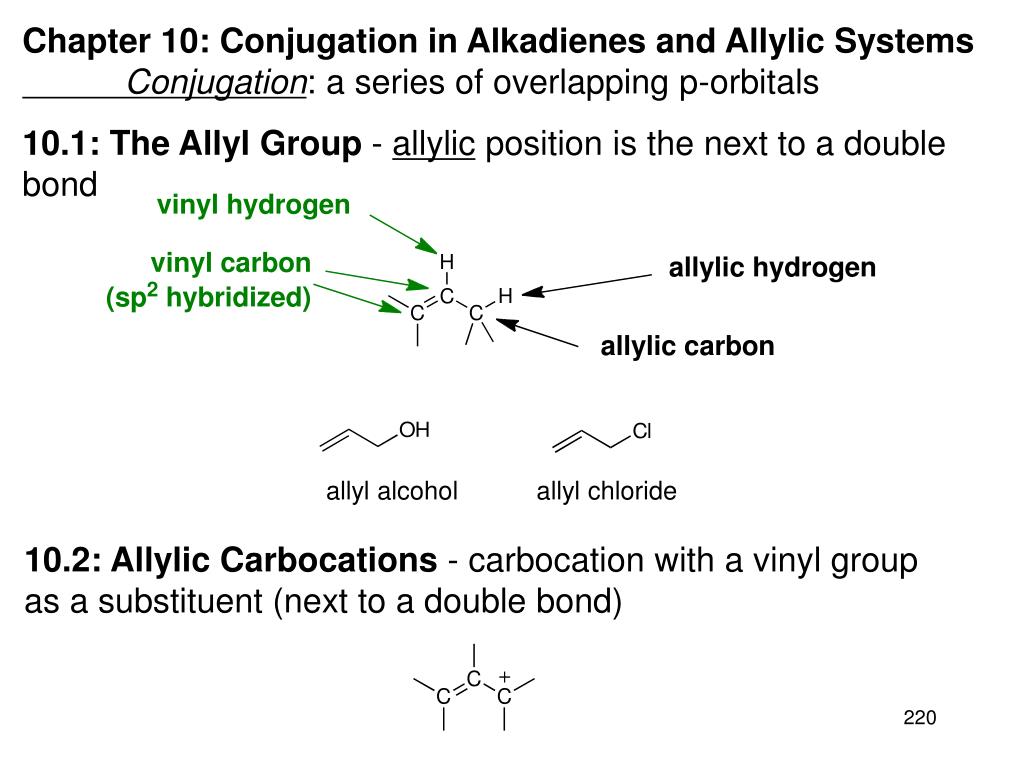
Allyl indicates a functional group with structural formula h 2 c ch ch 2 r where r is the rest of the molecule it consists of methylene bridge ch 2 in between the vinyl group ch ch 2 and the rest of the molecule therefore allyl group contains sp 2 hybridized vinyl carbon atoms and sp 3 hybridized allyl carbon atom. Allyl group consists of ch 2 methylene bridge and is attached with ch ch 2 vinyl group. Which of the following is an allylic halide. Benzylic allylic vinylic vinyl carbocations moreover are highly unstable whereas the other two are rather stable ones and the answer is c.
Allyl groups have three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms. Key difference allyl vs vinyl both allyl and vinyl groups have slightly similar structures with a small variation. The key difference between these two structural components is the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms. In allyl compounds where the next carbon is saturated but substituted once allylic rearrangement and related reactions are observed.
If next to an electron withdrawing group conjugate addition michael addition can occur. An allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula h 2 c ch ch 2 r where r is the rest of the molecule. Vinyl group vinylic hydrogen vinylic carbocation allylic position benzylic position propargylic position. The allylic carbon atom is more reactive than normal.