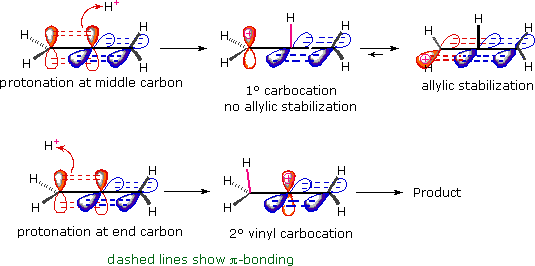
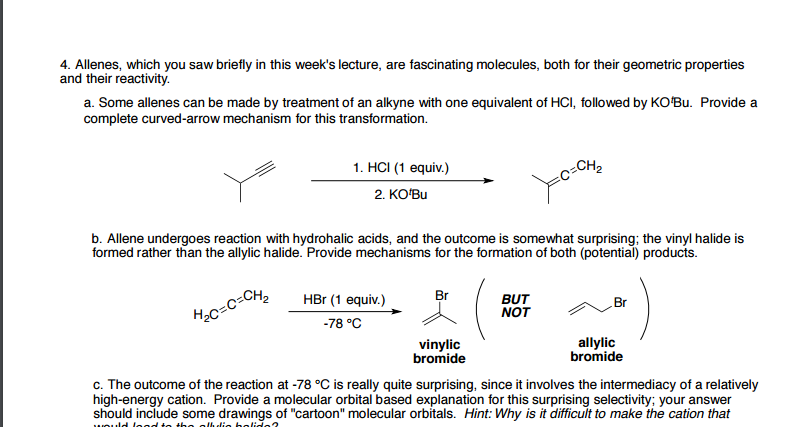
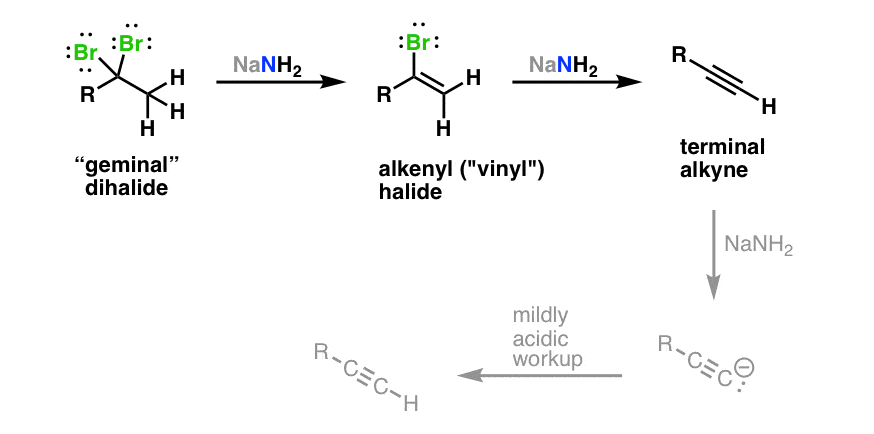
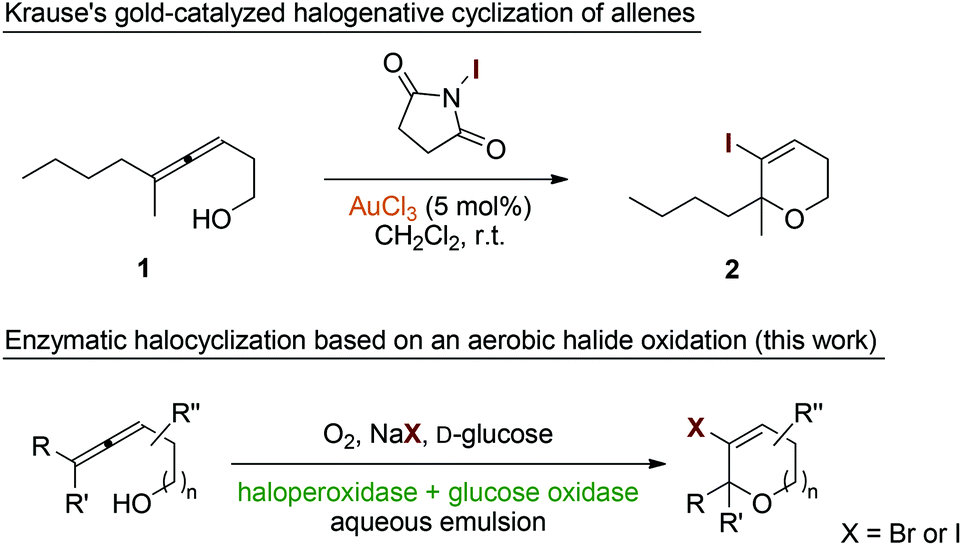
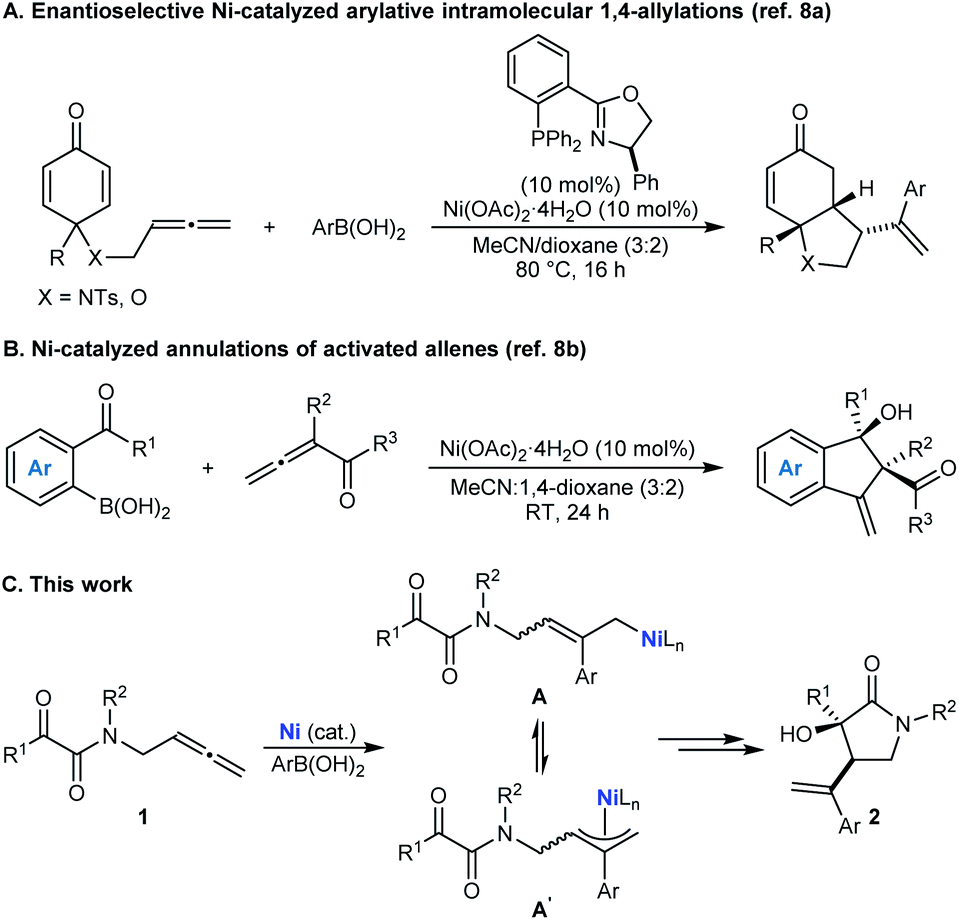
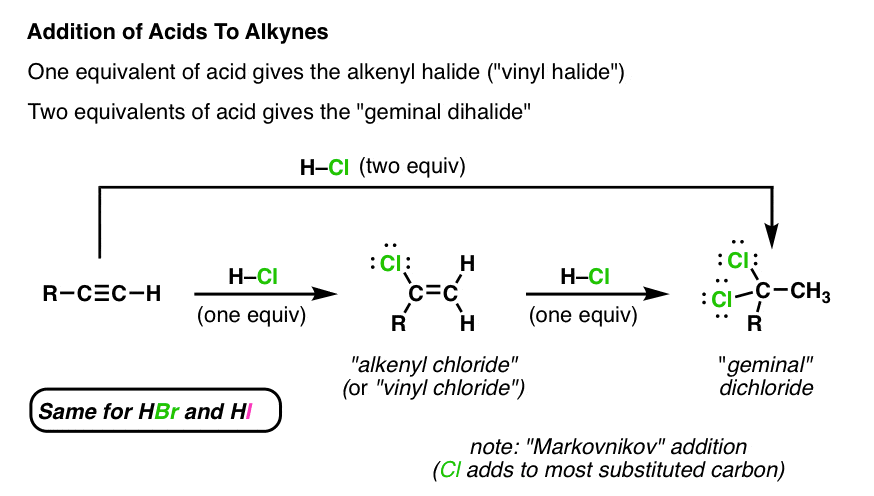Allene Vinyl Halide

A detailed discussion of these modifications is beyond the scope of this course but you.
Allene vinyl halide. Aryl or vinylpalladium halide addition to an allene also produces an η 3 allylpalladium halide suitable for amination. Vinyl cations have been observed as reactive intermediates during solvolysis reactions. It consists of a methylene bridge ch 2 attached to a vinyl group ch ch 2. The reaction of allene with a lower order silylcuprate 3 leads to an allylsilane vinylcopper intermediate 4 which undergoes palladium catalyzed cross coupling reaction with both vinyl and aryl halides.
However the experimental procedure can be modified so that this synthesis can be carried out using a wide range of alkyl aryl vinyl benzyl and allyl halides. In organic chemistry a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula ch 2 chx x halide. Generally vinylic halides are unreactive in solution. An allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula h 2 c ch ch 2 r where r is the rest of the molecule.
Silver nitrate does not precipitate silver halides in the presence of vinyl halides and this fact was historically used to dispute the existence of the vinyl cation species. The telomerization of allene with allyl and diallylamines yields secondary and tertiary alkadienylamines with up to 85 selectivity. Consistent with s n 1 chemistry these reactions follow first order kinetics. In order to obtain a good yield of alkane both r x and rx should be primary alkyl halides.