Alkyl Vinyl Aryl Acyl Halide Bonds
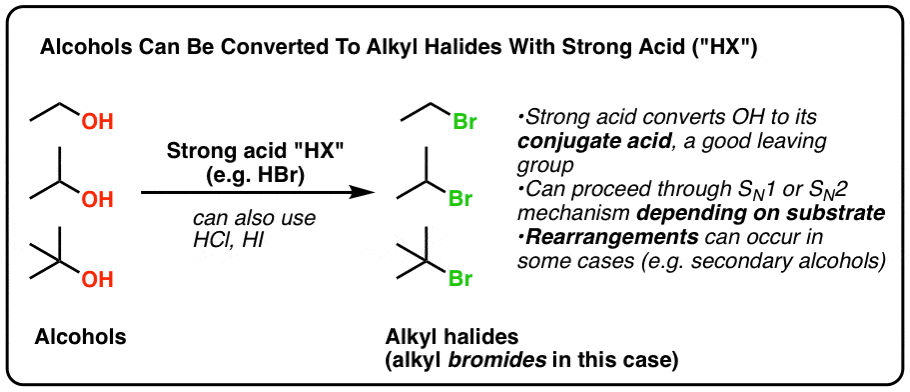
The attraction between the alkyl halide molecules is stronger than the attraction between the alkyl halide and water.
Alkyl vinyl aryl acyl halide bonds. Alkanoyl is usually derived from a carboxylic acid therefore it has the formula rc o where r represents an alkyl group that is linked to the carbon. In addition the carbon halogen bond is shorter and therefore stronger in aryl halides than in alkyl halides. In vinylic halides the carbon that bears the halogen is doubly bonded to another carbon. In alkyl halides all four bonds to the carbon that bears the halogen are single bonds.
The carbon chlorine bond in chlorobenzene is stronger than you might expect. In aryl halides the halogen bearing carbon is part of. An acyl group is a moiety derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid including inorganic acids it contains a double bonded oxygen atom and an alkyl group r c o. Are subdivided into alkyl vinylic aryl and acyl halides.
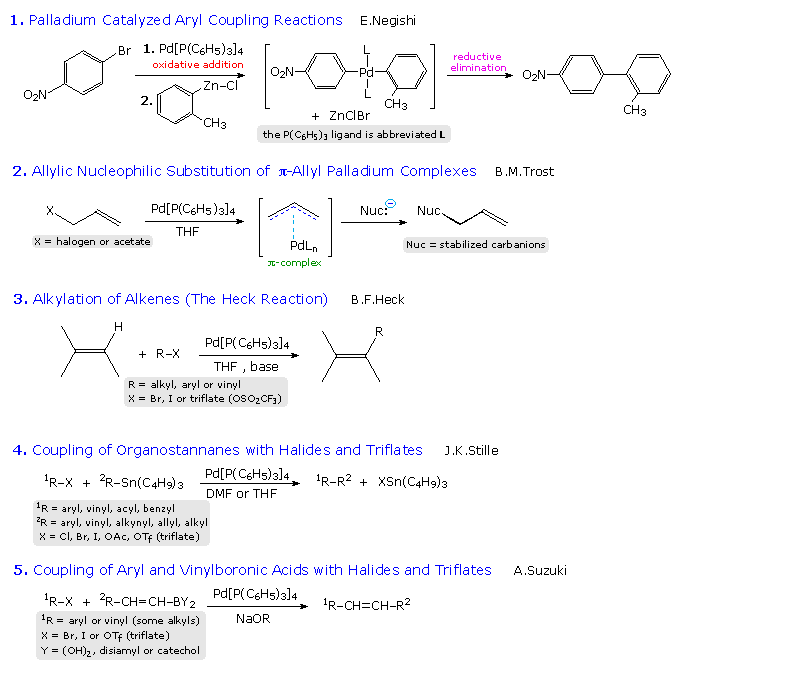
Alkyl groups and aryl groups are two examples of functional groups. Both alkyl and aryl groups have carbon and hydrogen atoms. Organometallic compounds are compounds that have a bond between a carbon and a metal atom. The halogen atom of an aryl halide atom could be exchanged for a metal atom using an organometallic reagent.
Halogen metal exchange of aryl halides. The carbon halogen bond is shortened in aryl halides for two. However alkyl halides may sometimes be confused with aryl halides. In organic chemistry the acyl group iupac name.
Other articles where aryl halide is discussed. Other articles where vinylic halide is discussed. An example of such reaction is the reaction between bromobenzene and an organolithium reagent where there. An aryl halide has general formula c 6h 5x in which an halide group x has substituted the aryl ring.
In alkyl halides all four bonds to the carbon that bears the halogen are single bonds. There is an interaction between one of the lone pairs on the chlorine atom and the delocalized ring electrons and this strengthens the bond. Halogens are more electronegative than carbon. Steric hindrance caused by the benzene ring of the aryl halide prevents s n 2 reactions.
Likewise phenyl cations are unstable thus making s n 1 reactions impossible. In vinylic halides the carbon that bears the halogen is doubly bonded to another carbon. For example if the halogen atom is attached to a carbon atom which is attached to a benzene ring cl ch 2 c 6 h 5 one would think it is an aryl halide but it is an alkyl halide because the halogen atom is attached to the carbon that is sp 3 hybridized. Alkyl halides have little to no solubility in water in spite of the polar carbon halogen bond.
The main difference between alkyl and aryl groups is that alkyl groups do not have aromatic rings whereas aryl groups have aromatic rings in their structure. In aryl halides the halogen bearing carbon is part of an. Alkyl halides have little to no solubility in water but be aware of densities.