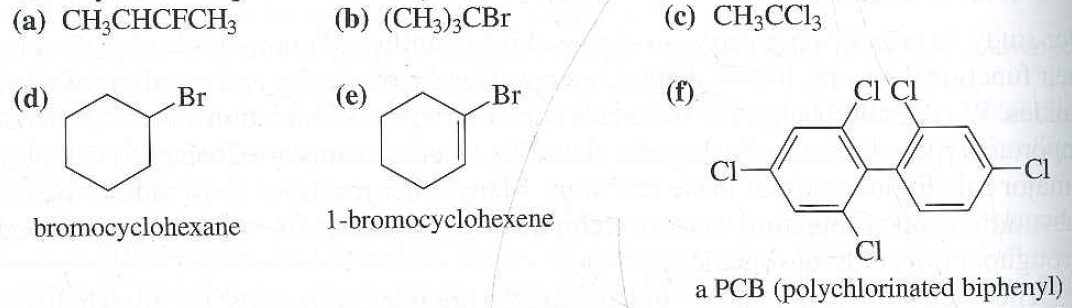
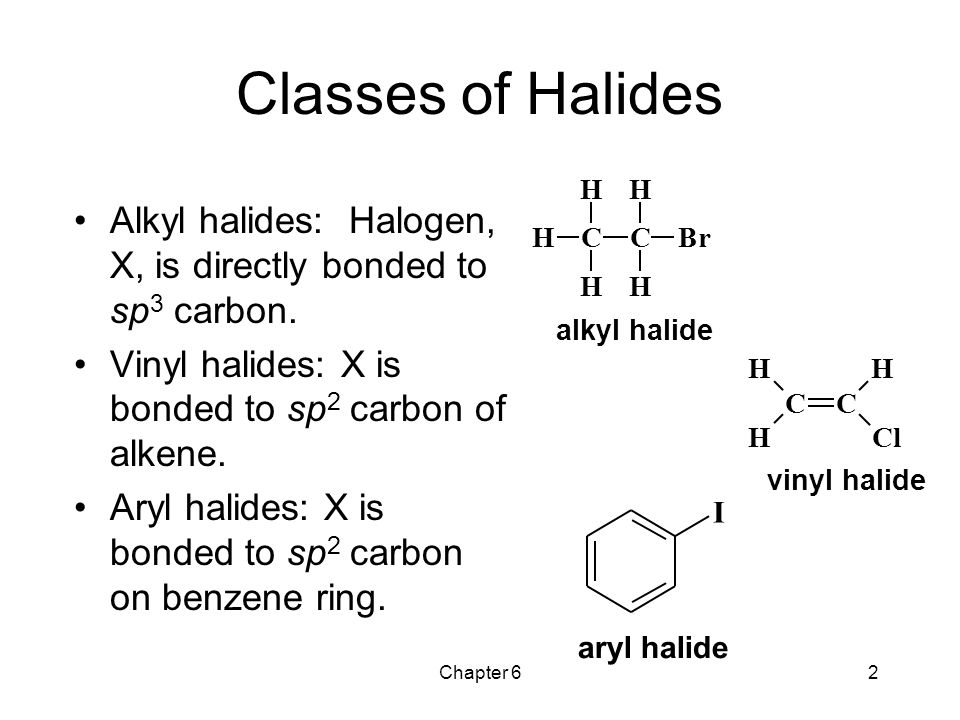
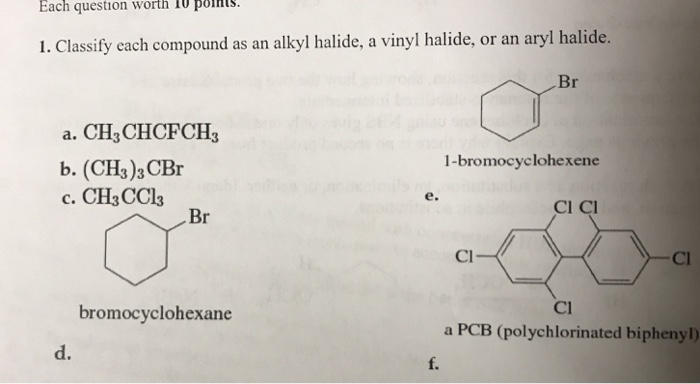
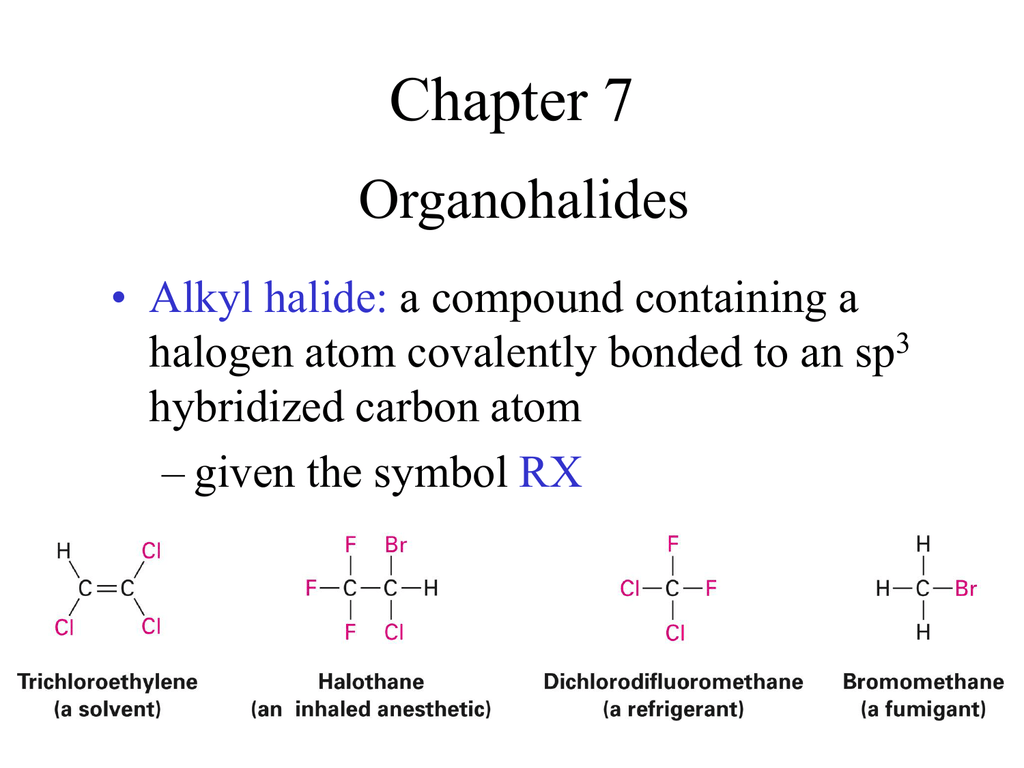
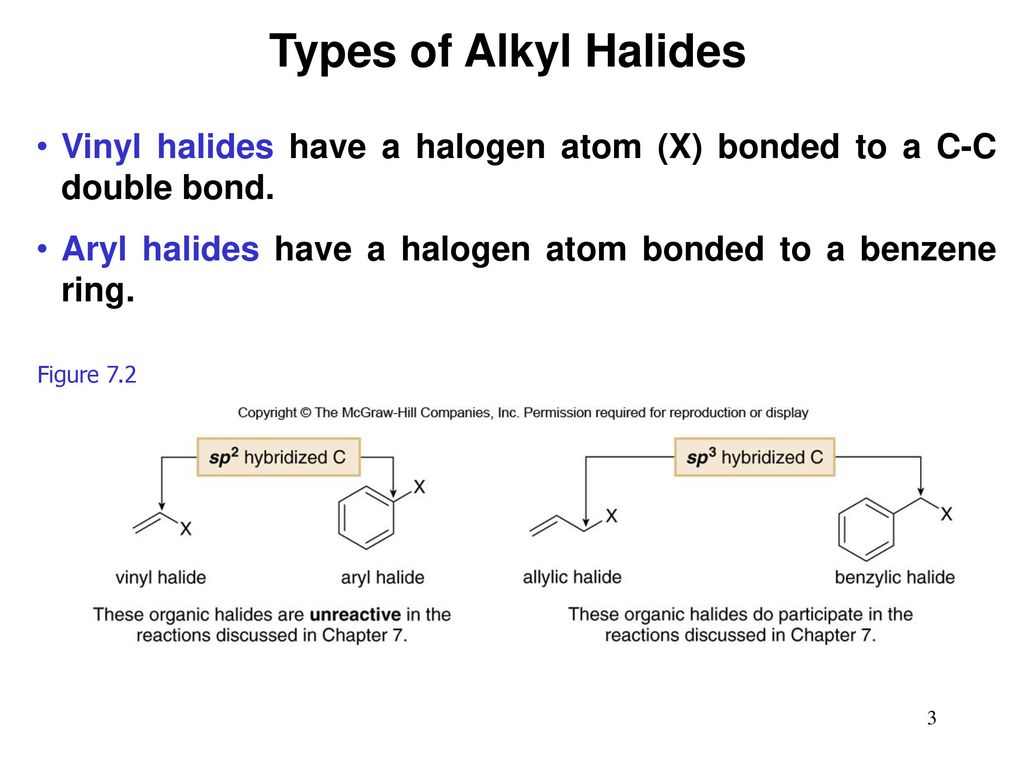
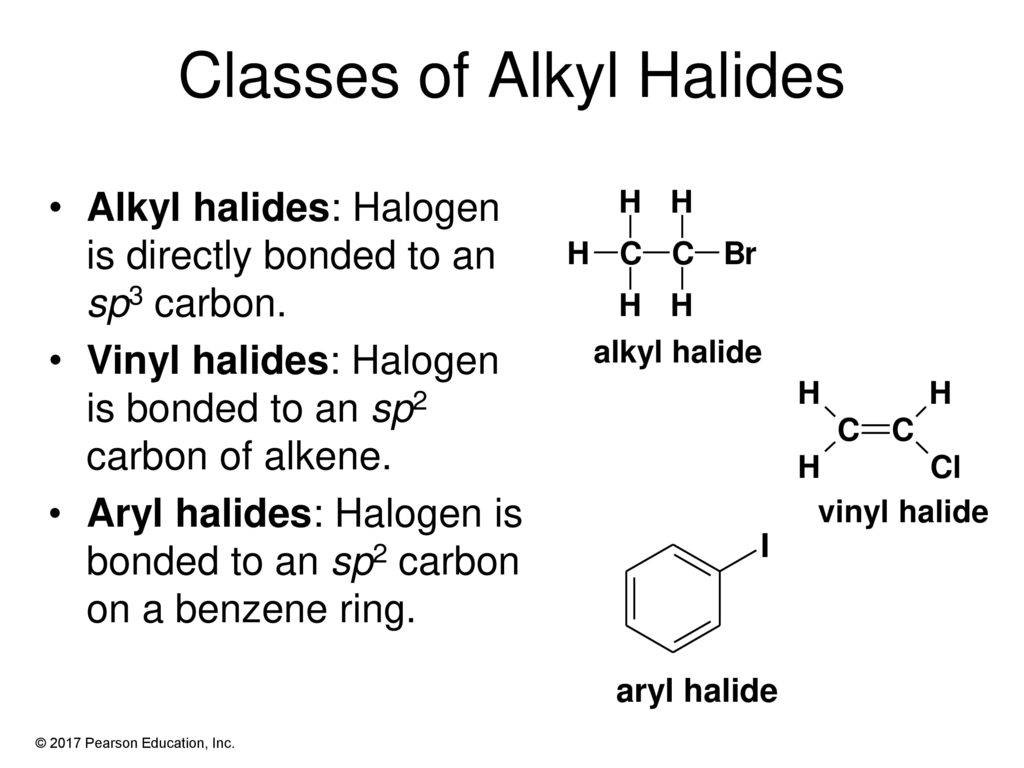
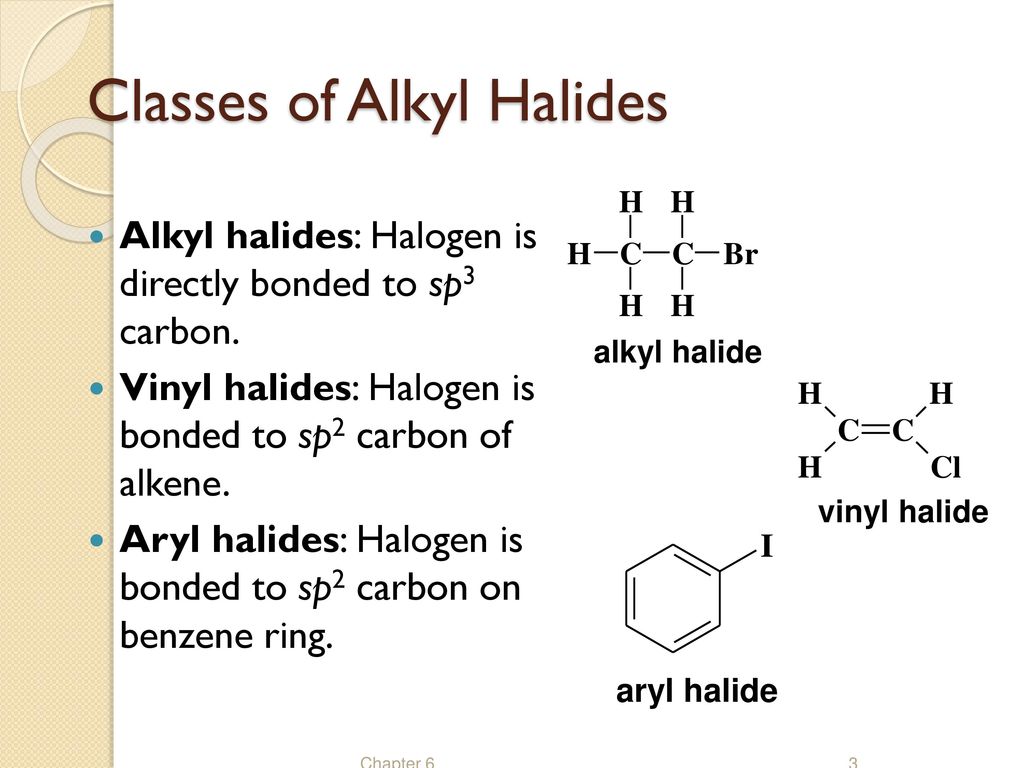
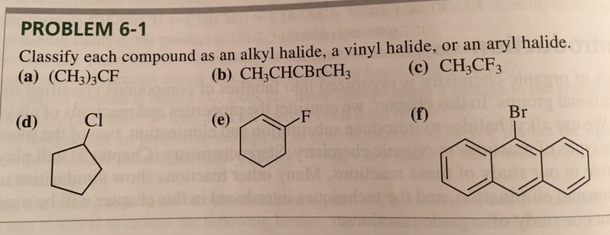Alkyl Halide Vinyl Halide Aryl Halide
For 3º halides a very slow s n 2 substitution or if the nucleophile is moderately basic e2 elimination.
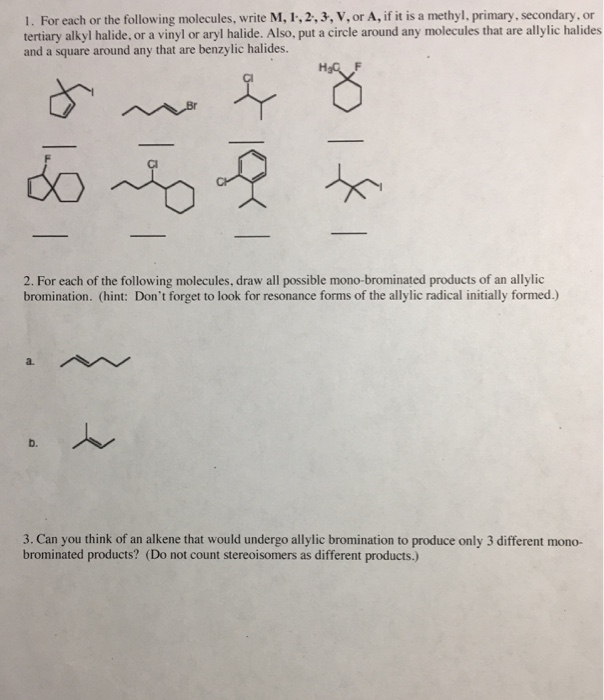
Alkyl halide vinyl halide aryl halide. Classify each compound as an alkyl halide a vinyl halide or an aryl halide. Walkthrough video for this problem. Fs show all steps. Steric hindrance caused by the benzene ring of the aryl halide prevents s n 2 reactions.
The carbon chlorine bond in chlorobenzene is stronger than you might expect. The extra strength of the carbon halogen bond in aryl halides. For example if the halogen atom is attached to a carbon atom which is attached to a benzene ring cl ch 2 c 6 h 5 one would think it is an aryl halide but it is an alkyl halide because the halogen atom is attached to the carbon that is sp 3 hybridized. Halogens are more electronegative than carbon.
The carbon halogen bond is shortened in aryl halides for two. In high dielectric ionizing solvents such as water dimethyl sulfoxide acetonitrile s n 1 and e1 products may be observed. There is an interaction between one of the lone pairs on the chlorine atom and the delocalized ring electrons and this strengthens the bond. Chapter 6 problem 1p 7 43 1 0.
Step 1 of 5. 100 44 ratings for this solution. In addition the carbon halogen bond is shorter and therefore stronger in aryl halides than in alkyl halides. An aryl halide has general formula c 6h 5x in which an halide group x has substituted the aryl ring.
Likewise phenyl cations are unstable thus making s n 1 reactions impossible. A vinyl halide is clearly a species with a formula h 2c c x h in which a halide is directly bound to an olefinic bond formally this is ethylene h 2c ch 2 with one of the hydrogens substituted by a heteroatom vinyl chloride h 2c chcl is an example.