Air Resistance Against A Marble

M s 2 unit system.
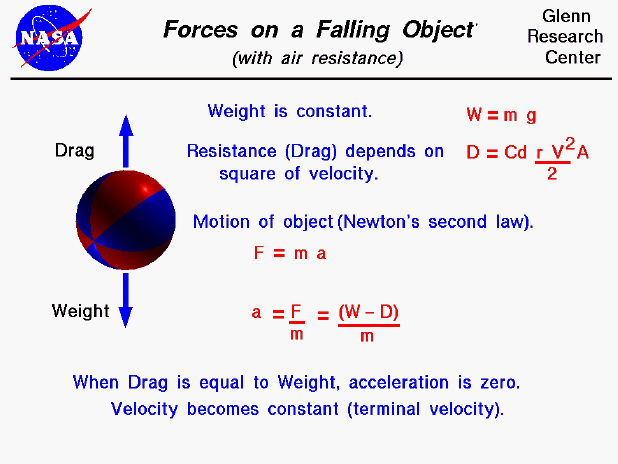
Air resistance against a marble. The density of air ρ. Gravity and air resistance explained. Air and fluid resistance. Motion of many objects.
There are other stories based on legends about. Chinese acrobats also used parachutes of some kind to perform falling stunts. Google classroom facebook twitter. Neglecting air resistance the horizontal component velocity of a projectile that moves along the path of a parabolic curve will remain constant neglecting air resistance what trajectory angle measured from the horizon will result in the greatest horizontal distance traveled by a projectile.
Net force downwards mg drag due to air resistance. So 1st 2nd 4th are all valid. Suppose further that in addition to the force of gravity the projectile is subject to an air resistance force which acts in the opposite. Free fall time t.
Charged particle motion in up. Free fall velocity v f r e e f a l l 1 h 1 2 g t 2 2 v g t f r e e f a l l 1 h 1 2 g. Free fall distance h. This typically has a value around 1 2 kg m 3.
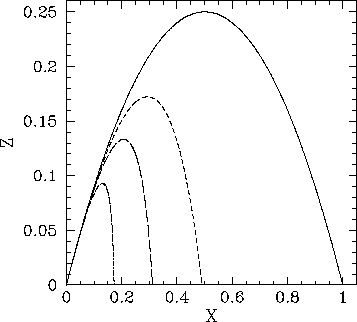
The cross sectional area of the object a a ping pong ball would have a cross sectional area equal to π r 2. The force of air resistance f n on a 0 10 kg marble dropped from a great height is shown on the graph below plotted against the distance fallen x m. Air and fluid resistance. This is the currently selected item.
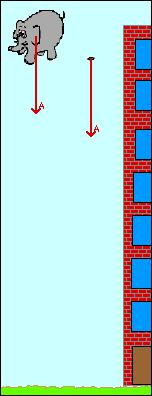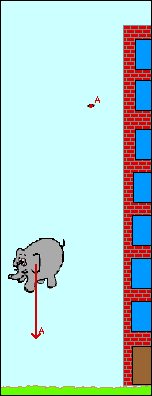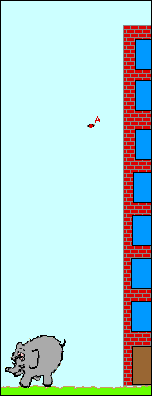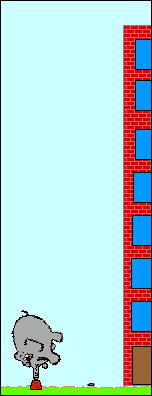
The use of air resistance to slow down a fall can be dated back to 90 b c. Motion in a two dimensional projectile motion with air resistance suppose that a projectile of mass is launched at from ground level in a flat plain making an angle to the horizontal. If you tried dropping paper and a lego brick or similar the paper should have dropped to the floor more slowly than the brick this is because the paper has a larger surface area so has to push against more air as it drops which means the air resistance is greater and it drops more slowly. Feather has less mass than the marble and the drag air resistance will be more because of its shape so drag m will be greater than for the marble so acceleration less so marble reaches the ground first.
O 8 a calculate the work done by gravity on the marble 0 6 after the first meter of fall 0 4 l0 2 b calculate the work done by air resistance in the first 5 meters of the fall. Calculates the free fall distance and velocity without air resistance from the free fall time. Modeling gravity and friction. According to chinese historian si ma chian a legend described an emperor using two bamboo hats to jump off a roof and land safely on the ground.